Efficient Machining Through the Right Choice of Carbide Grade
Selecting the right carbide grade is important for achieving maximum efficiency in machining. While most grades work well in various materials, a careful choice for your specific material can provide significant advantages.
FourCut Carbide Grades
Choose between two different grades for the best possible productivity. SmiCut’s complete range of FourCut inserts for thread turning and grooving is available in both grades.
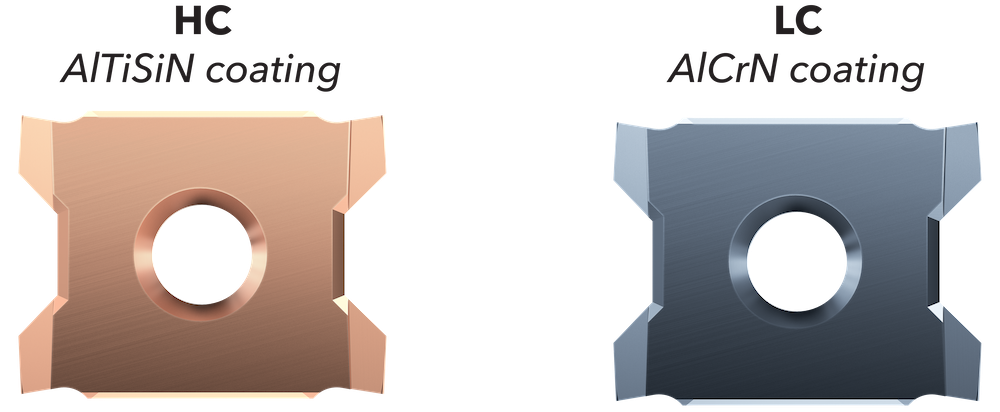
HC is a carbide grade with AlTiSiN coating. It is particularly suitable for harder materials and high-temperature applications.
LC is a carbide grade with AlCrN coating. It offers a good balance between toughness and heat resistance.
Choose Your Grade
Check out the table below to help you select the optimal carbide grade for FourCut inserts based on the material you are machining. This information is also available as a PDF.
(If you cannot see the entire table, rotate your phone to landscape mode.)
HB
N/mm²
Choice
Choice